
Most Commonly Used Project Management Techniques Explained
Introduction
The start of a project is the most important phase. How you distribute the work and configure the processes will determine your ultimate success.
The world of project management is huge. It covers many industries and requires a range of skills. But the common thread that connects this diverse discipline is the techniques used by project managers to get the job done.
Project management techniques make planning and managing projects easier and more efficient. They can be applied to any project, regardless of industry or branch. Combined with project management software, they save time and reduce costs.
As with many things, there are several ways to approach the project management process. There is no one-size-fits-all here, so each method adds something unique to your project. To help you choose a methodology for your next project and to provide you with new tools and ideas, here are some project management techniques you can use in your project.
Explore These Intriguing Reads Just for You–
- Unlock Project Management Excellence with PMP Certification
- Everything you need to know about Transferable Development Rights
- The Ultimate Guide to Different Business Structures
- Best Practices to Prevent Accidents on the Job Site
- How to Properly Handle and Store Construction Materials on Site
1. Work Breakdown Structure (PSP)
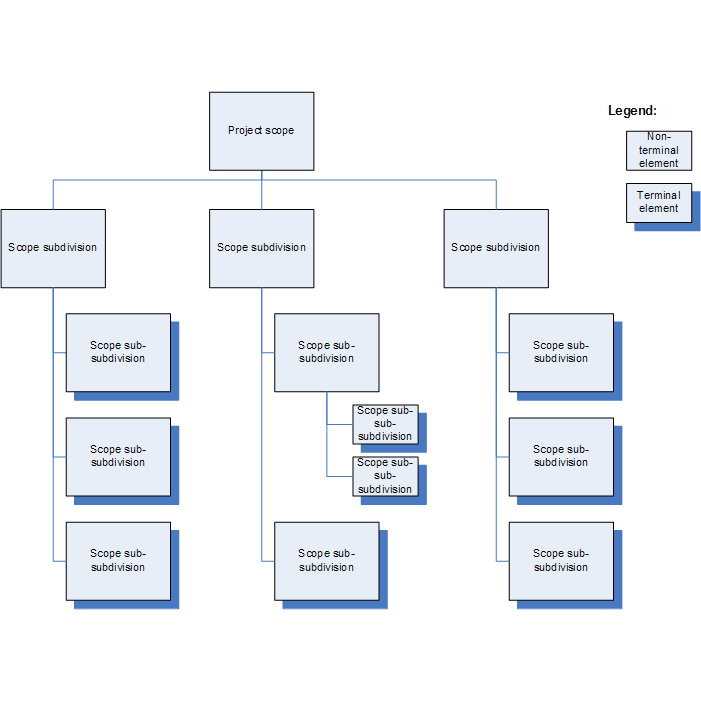
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a way to organize work into smaller, more manageable parts. According to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK), the WBS is a “deliverable-oriented hierarchical breakdown of work to be done by the team.”
This means that the PSP is a graphical representation of each task in the project. At the top is the final product with a line running down the side to one or more boxes that represent the more important tasks that lead to that completed project. Each of these boxes is then attached with lines that run underneath for smaller tasks.
So, if you were to build a house like in the example above, you would divide the work into segments such as internal work, external work, and construction of the foundation. From there, you would further divide the work into work packages based on task levels and dependencies.
WBS can be used as a project management technique, but it can also be a tool, whatever technique you ultimately choose. It will help you understand all the tasks and resources required to create the final performance.
2. Critical path method (CPM)
The critical path method has been a cornerstone of the project management plan since the 1940s. CPM requires that you create a project template that includes a list of all tasks or a WBS, the time required to complete each of these. tasks, and, if applicable, the duration and any external factors that may affect each milestone.
CPM is an algorithm that helps in decision-making. By recording specific data (start time, duration, end time), determines which activities are most critical to the success of the project. CPM is best for more complex projects with many task dependencies.
Overall, CPM helps reduce delays by optimizing work along the critical path. It can also view dependencies, which helps prioritize tasks. CPM improves organization by dividing results into sequences. It increases efficiency and helps calculate the float to better distribute resources.
3. Program evaluation and review technique (PERT)

PERT stands for Program Evaluation and Review Technique. It is a project management technique that helps in time estimation. Planning is of course crucial to complete a project on time, but also budget. The longer you work, the more you pay. PERT breaks down tasks into detailed activities, by using the WBS discussed above, then adds these to a Gantt chart to identify those activities that are interdependent.
The PERT technique is widely preferred because of its visualization component. Graphics are used to graphically represent the timeline of a project and make it easy to understand at a glance. The PERT method allows you to create a detailed plan and then visually track milestones and progress in the form of a graph.
The PERT method is best for long-term projects where a physical schedule is useful or for larger projects with particular challenges. These charts make it easier for you to assess time, resources, and plans during a project.
4. Waterfall

The waterfall approach suggests a sequential approach to project management. Once stakeholders and clients agree on and document the project requirements, the project is carried out step by step through to completion. After that, the client reviews the project to make sure it meets the requirements. Some projects require a post-production maintenance phase, eg. B. Software project in which the client reports errors and requests new functions to ensure lasting performance and success of the project.
The waterfall is ideal for projects with different phases that require very few iterations throughout the project lifecycle. If you think there are some things you need to change and re-discuss the scope or budget of the project, Waterfall is not for you. The most popular tool for the waterfall model is the Gantt chart, which visualizes project subtasks, dependencies, and phases during the project lifecycle.
5. Kanban – The easiest project management technique

The Kanban project management technique was developed by a Toyota engineer to improve the manufacturing process and is based on teamwork and the fundamentals of project management. It’s a visual workflow, like PERT, but unlike the graphical nature of PERT, configured as a series of task cards.
Kanban is an ideal project management technique for overall management as it promotes continuous delivery and less stress for individual members. It values effective teamwork and is designed as a visual project board, perfect for plans that require many steps with many teammates.
Join Our Whatsapp Group for the latest updates -Click Here
Join Our Telegram Channel for the latest updates -Click Here